What’s the big issue regarding sustainable plastics, and are you asking why? Let’s take a closer look at poly lactide acid (PLA), a revolutionary material in the plastics sector that is causing an uproar in the appropriate places. The phrase “PLA” is a positive indicator that the world is becoming more ecologically friendly. So why is PLA so important in today’s world?
How does polylactide work?
PLA, referred to as poly lactide, is a kind of bioplastic made from renewable sources like sugarcane or wheat grain. For regular plastics, which are made from petroleum, PLA gives a biodegradable and compostable green option.
Renewable Polymers: Their Value
In an age where waste and warming temperatures pose significant concerns, it is crucial to transition to sustainable materials. The lengthy biodegradation period of conventional plastics creates considerable harm to the environment. The ecological impact of PLA declines however, as it breaks down much more quickly.
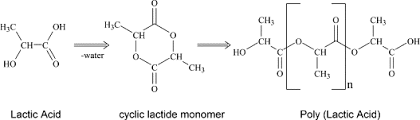
The Polylactide’s Chemistry
The composition and structure
PLA is produced by the process of fermentation of lactic acid, a polymer that comes from naturally occurring sugars. Thus, PLA has special characteristics such as composting and breakdown in a manufacturing setting.
Method of Synthesis
For the production of PLA, polymer of lactic acid is carried out by a method called ring- opening polymerization. This approach ensures that the final plastic will continue to have the pliability and durability needed for an array of uses.
The Historic and Present Survey and Findings
PLA began in the 1930s when researchers started investigating ways of producing polymers from resources that are renewable. Yet, PLA did not gain momentum on a commercial basis till the late 20th century, because of advances in biotechnology.
Variations in Polylactone Production Through Time
Manufacturing of PLA has shifted considerably as awareness of the environment has grown. PLA has become increasingly available and reasonably priced due to the massive manufacturing made possible by modern methods.
Poly Lactide Applications
The Packaging Sector
From food containers to disposable cutlery, PLA is widely used in packaging. Because of its strength and transparency, it is the perfect material for packaging applications.
Health Care Sector
PLA finds application in the medical field in the areas of implants, drug delivery systems, and sutures. Interacting with human tissues in a safe manner is guaranteed by its biocompatibility.
Applications in Agriculture
PLA is utilized in agriculture to create mulch films that enrich the soil and decrease waste by decomposing after use.
Compare Polymers That Were Common
Polyethylene with Propylene.
Polyester and polyethylene, or PE, are example of conventional plastics created from petroleum and coal (PP). While they are strong and flexible, their impact on the environment is an important concern.
Environmental Impact: When compared the environmental advantages of PLA with those of Pp and PP, PLA undoubtedly emerges as the victor. Its lower carbon footprint and the biodegradability make it a more sustainable option.
Walls and Limits
Manufacturing Expenditures
One of PLA’s primary problems is that it can be more expensive for manufacturing than conventional polymeric materials. But as technology advances, costs should drop.
Mechanical characteristics
PLA can be utilised in numerous uses, but it is not as durable as some other frequently used polymers, thus it shouldn’t be used in high-stress situations.
Reusing and Managing Waste
PLA can be composted, but only under certain circumstances will it break down effectively. This presents difficulties for recycling and waste management systems.
Market Trends and Prospects for the Future
Present-day Market Situation
The growing need for sustainable materials is propelling the PLA market’s rapid growth. Businesses throughout an array of industries utilise PLA to try fulfil regulatory and consumer demands for products that are environmentally friendly.
Opportunities for Further Growth
With significant growth anticipated in the following years, PLA has an exciting future. New developments and increased production capacity are probably going to drive the expansion.
Encouraging Eco-Friendly Choices
Educating consumers on the advantages of PLA and environmentally friendly alternatives is imperative. This may encourage the market for environmentally friendly goods and help environmental programs.
Learning’s Part in Decreasing Plastic Use
It is mainly the duty of schools and efforts to broaden the public’s awareness of the issues caused by plastic pollution and the advantages of sustainable alternatives like PLA.
Conclusion,
Poly lactide is a significant step forward in the quest for sustainable materials. Because of its numerous applications, positive impact on the environment, and increasing share of the market, it will be important to the plastics industry in the future. We may decrease the planet’s effect and work towards a future that is healthier by using PLA.
FAQs
- What components make up polylactide?
- Corn starch or sugarcane are examples of renewable resources that are used to make poly lactide.
- How biodegradable is PLA?
- In industrial composting settings, PLA does indeed biodegrade.
- Which are PLA’s primary applications?
- Packaging, textiles, electronics, and agriculture all use PLA.
- Why is PLA distinct from conventional plastics?
- PLA has little of an impact on the environment since it is recyclable and depends on resources that are renewable.
- Which difficulties arise when using PLA?
- Using PLA presents a number of challenges, including higher production costs and particular composting requirements.